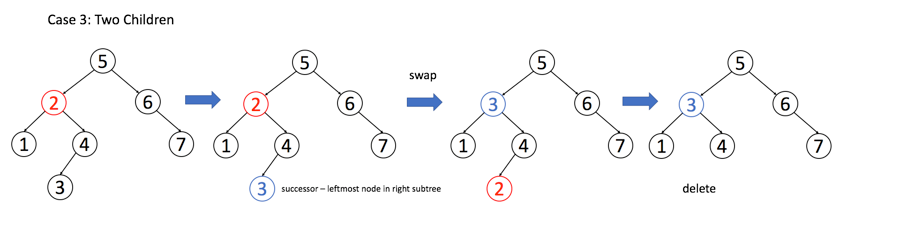
Delete Node in a BST
root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7]
key = 3
5
/ \
3 6
/ \ \
2 4 7
Given key to delete is 3. So we find the node with value 3 and delete it.
One valid answer is [5,4,6,2,null,null,7], shown in the following BST.
5
/ \
4 6
/ \
2 7
Another valid answer is [5,2,6,null,4,null,7].
5
/ \
2 6
\ \
4 7Solution
Last updated