N-ary Tree
A binary tree is a rooted tree in which each node has no more than 2 children. Let's extend this definition toN-ary tree. If a tree is a rooted tree in which each node has no more thanNchildren, it is calledN-ary tree.
Here is an example of 3-ary tree:
Trieis one of the most frequently used N-ary trees.
Also, a binary tree is a special form of a N-ary tree. In the following sections, we will extend what we have learned about binary trees to N-ary trees.
A binary tree can be traversed in preorder, inorder, postorder or level-order. Among these traversal methods, preorder, postorder and level-order traversal are suitable to be extended to anN-arytree.
Retrospect - Traverse a Binary Tree
Preorder Traversal: Visit the root node, then traverse the left subtree and finally traverse the right subtree.
Inorder Traversal: Traverse the left subtree, then visit the root node and finally traverse the right subtree.
Postorder Traversal: Traverse the left subtree, then traverse the right subtree and finally visit the root node.
Level-order Traversal: Traverse the tree level by level.
Note that here is no standard definition for in-order traversal in n-ary trees. It probably only makes sense for binary trees. While there are several different possible ways that one could define in-order traversal for n-ary trees, each of those feels a bit odd and unnatural and probably not terribly useful in practice.
To generalize the above to n-ary trees, you simply replace the steps:
Traverse the left subtree.... Traverse the right subtree....
in the above by:
For each child: Traverse the subtree rooted at that child by recursively calling the traversal function
We assume that the for-loop will iterate through the children in the order they are found in the data-structure: typically, in left-to-right order, for a diagram such as below.
N-ary Tree Traversal Examples
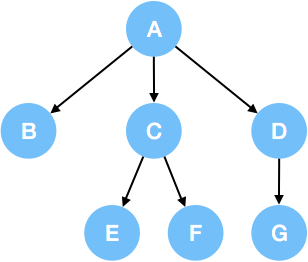
We will use the following 3-ary tree as example:

1. Preorder Traversal
In an N-ary tree, preorder means visit the root node first and then traverse the subtree rooted at its children one by one. For instance, the preorder of the 3-ary tree above is: A->B->C->E->F->D->G.
2. Postorder Traversal
In an N-ary tree, postorder means traverse the subtree rooted at its children first and then visit the root node itself. For instance, the postorder of the 3-ary tree above is: B->E->F->C->G->D->A.
3. Level-order Traversal
Level-order traversal in an N-ary tree is the same with a binary tree. Typically, when we do breadth-first search in a tree, we will traverse the tree in level order. For instance, the level-order of the 3-ary tree above is: A->B->C->D->E->F->G.
Last updated